Embark on a captivating journey into the realm of metamorphic rocks, where the metamorphic rock worksheet answer key serves as your guide. This comprehensive resource unlocks the secrets of these enigmatic rocks, revealing their diverse types, intriguing processes, and fascinating structures.
Prepare to delve into the very essence of Earth’s geological transformations.
Metamorphic rocks hold a wealth of information about our planet’s dynamic history. They bear witness to the profound changes that have shaped the Earth’s crust, providing valuable insights into the forces that have molded our landscapes and influenced the evolution of life.
Metamorphic Rock Types
Metamorphic rocks are formed when existing rocks are subjected to intense heat, pressure, and chemical alteration within the Earth’s crust. These processes can transform the original rock into a new rock with a different composition, texture, and structure.
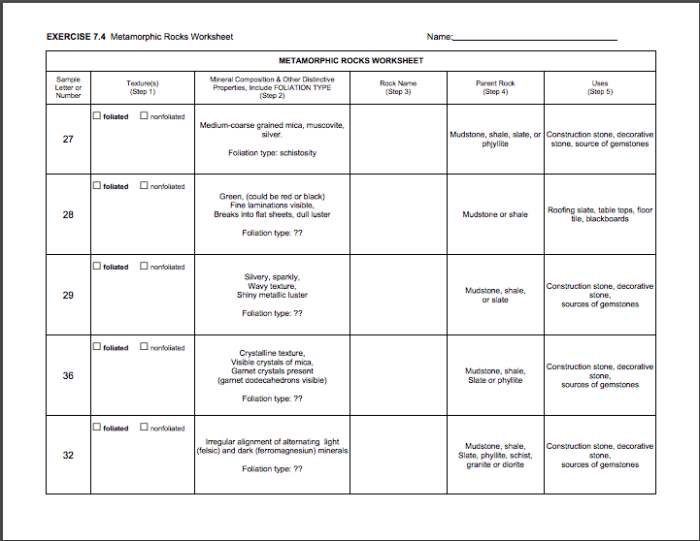
Foliated Metamorphic Rocks, Metamorphic rock worksheet answer key
- Slate: Fine-grained, composed of clay minerals, with a distinct slaty cleavage.
- Phyllite: Finer-grained than slate, with a silky sheen and a more pronounced foliation.
- Schist: Coarse-grained, with a well-developed foliation due to the alignment of platy minerals like mica.
- Gneiss: Coarse-grained, with alternating bands of light and dark minerals, resembling granite.
Non-foliated Metamorphic Rocks
- Marble: Formed from limestone, composed primarily of calcite or dolomite, with a sugary texture.
- Quartzite: Formed from sandstone, composed primarily of quartz, with a glassy texture.
- Hornfels: Formed from fine-grained igneous or sedimentary rocks, with a compact, non-foliated texture.
Metamorphic Processes
Metamorphism occurs when rocks are subjected to changes in temperature, pressure, and chemical composition within the Earth’s crust. These changes can be caused by various geological processes, such as:
- Contact metamorphism: Occurs when magma or hot fluids come into contact with existing rocks.
- Regional metamorphism: Occurs when large areas of rock are subjected to high temperatures and pressures over a long period of time.
- Hydrothermal metamorphism: Occurs when hot, chemically active fluids circulate through rocks, altering their composition.
Metamorphic processes involve the recrystallization of minerals, the formation of new minerals, and the alteration of the rock’s texture and structure.
Metamorphic Rock Structures

Metamorphic rocks exhibit a wide variety of structures, including:
- Foliation: A layering or banding caused by the alignment of platy minerals.
- Lineation: A linear arrangement of minerals or other features.
- Schistosity: A foliation that is particularly well-developed, with a strong preferred orientation of platy minerals.
- Gneissic banding: A foliation that is characterized by alternating bands of light and dark minerals.
These structures provide valuable information about the metamorphic history of the rock, such as the temperature, pressure, and fluid conditions under which it formed.
Metamorphic Rock Environments
Metamorphic rocks can be found in a variety of geological environments, including:
- Contact metamorphic zones: Areas around igneous intrusions where rocks have been heated and altered by the intrusion.
- Regional metamorphic belts: Large areas of rock that have been subjected to high temperatures and pressures over a long period of time.
- Subduction zones: Areas where one tectonic plate is moving beneath another, causing the rocks on the subducting plate to be heated and metamorphosed.
The type of metamorphic rock that forms in a particular environment depends on the temperature, pressure, and chemical composition of the rocks involved.
Metamorphic Rock Applications

Metamorphic rocks are used in a variety of industries, including:
- Construction: Marble and granite are used as building materials and decorative stones.
- Road construction: Quartzite and gneiss are used as aggregate in road construction.
- Industrial processes: Metamorphic rocks are used as raw materials in the production of cement, glass, and ceramics.
- Jewelry: Marble and other metamorphic rocks are used in jewelry making.
Metamorphic rocks are valued for their durability, aesthetic appeal, and industrial applications.
FAQ Section: Metamorphic Rock Worksheet Answer Key
What are the main types of metamorphic rocks?
Metamorphic rocks are classified into three main types: foliated, non-foliated, and cataclastic.
What is the difference between foliated and non-foliated metamorphic rocks?
Foliated metamorphic rocks exhibit a layered or banded appearance due to the alignment of minerals, while non-foliated metamorphic rocks lack this distinct layering.
What is the role of heat and pressure in metamorphism?
Heat and pressure are the primary driving forces behind metamorphism. They cause the minerals in the original rock to recrystallize and form new minerals that are stable under the new conditions.