Glucocorticoid response elements function as enhancers. – Glucocorticoid response elements function as enhancers, playing a crucial role in gene regulation. These elements, found in the DNA of target genes, interact with glucocorticoid receptors to modulate transcription, influencing a wide range of physiological processes.
The molecular structure and function of GREs, their role in enhancing gene transcription, and the factors that regulate their activity are key aspects of this discussion. Additionally, the clinical significance of GREs in diseases such as asthma and inflammation highlights their potential therapeutic implications.
Introduction: Glucocorticoid Response Elements Function As Enhancers.
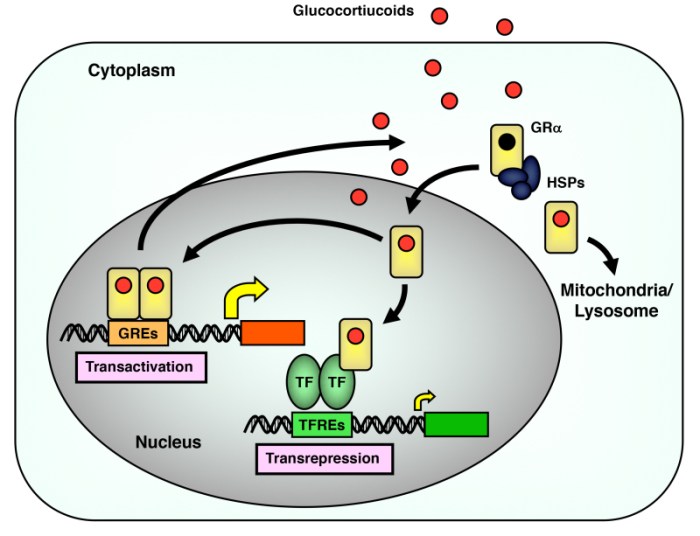
Glucocorticoid response elements (GREs) are DNA sequences that mediate the transcriptional regulation of genes by glucocorticoids, a class of steroid hormones. GREs are essential for the physiological effects of glucocorticoids, which include anti-inflammatory, immunosuppressive, and metabolic actions.
Structure and Function of GREs
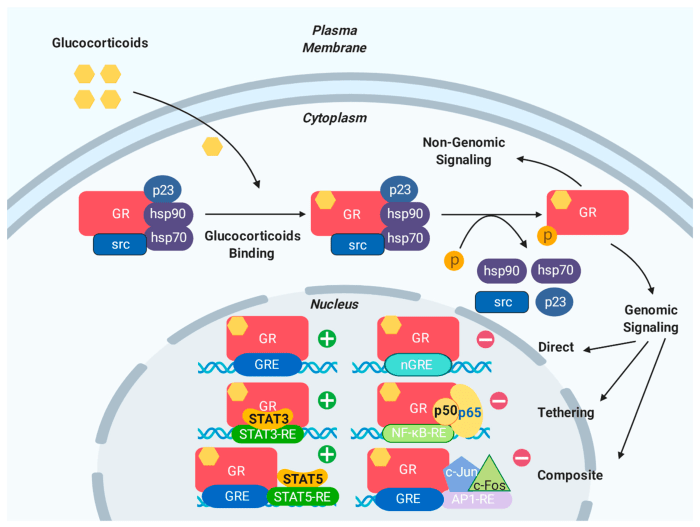
GREs are typically palindromic sequences of 15-20 nucleotides that contain the core sequence AGAACA. GREs are located in the promoter regions of target genes and are recognized by glucocorticoid receptors (GRs), which are ligand-activated transcription factors. Upon binding to GREs, GRs undergo a conformational change that allows them to recruit coactivators and corepressors, which modulate the transcriptional activity of the target gene.
GREs as Enhancers
GREs function as enhancers, which are DNA sequences that increase the rate of transcription of a gene. GREs can be located upstream or downstream of the transcription start site and can interact with other regulatory elements, such as promoters and silencers, to fine-tune gene expression.
Regulation of GRE Activity
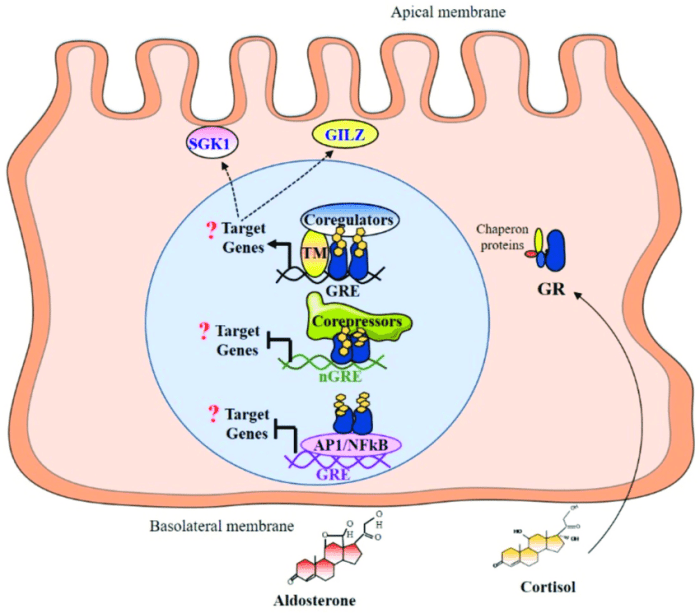
The activity of GREs is regulated by a variety of factors, including the concentration of glucocorticoids, the presence of coactivators and corepressors, and the methylation status of the DNA surrounding the GRE.
Clinical Significance of GREs, Glucocorticoid response elements function as enhancers.
GREs are involved in a variety of diseases, including asthma, inflammation, and cancer. Dysregulation of GRE activity can lead to abnormal gene expression and contribute to disease pathogenesis.
Experimental Techniques for Studying GREs
A variety of experimental techniques are used to study GREs, including chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP), electrophoretic mobility shift assays (EMSA), and luciferase reporter assays.
Future Directions in GRE Research
Future research on GREs will focus on understanding the molecular mechanisms of GRE regulation and the role of GREs in disease pathogenesis. This research will lead to the development of new therapeutic strategies for diseases involving GRE dysregulation.
Essential Questionnaire
What are glucocorticoid response elements (GREs)?
GREs are specific DNA sequences that bind glucocorticoid receptors, regulating gene transcription in response to glucocorticoid hormones.
How do GREs enhance gene transcription?
GREs recruit coactivators to the promoter region of target genes, facilitating the assembly of the transcription machinery and enhancing RNA polymerase activity.
What is the clinical significance of GREs?
GREs are implicated in various diseases, including asthma and inflammation. Dysregulation of GRE activity can contribute to disease pathogenesis and therapeutic resistance.