Federalism and the Division of Power Worksheet offers a comprehensive exploration of the intricate balance of authority within federal systems. This worksheet delves into the fundamental principles, historical evolution, and practical implications of power distribution, providing a valuable resource for students and practitioners alike.
Through a combination of clear explanations, thought-provoking examples, and insightful analysis, this worksheet guides learners through the complexities of federalism, empowering them to critically assess the division of power and its impact on governance.
Definition and Overview of Federalism
Federalism is a system of government in which power is divided between a central authority and several regional or state governments. This division of power is typically based on a written constitution that establishes the respective powers of each level of government.
Federalism has been adopted by numerous countries around the world, including the United States, Canada, Australia, and Germany. The historical development of federalism in these countries has varied, but the underlying principles remain largely the same.
Division of Powers in a Federal System: Federalism And The Division Of Power Worksheet
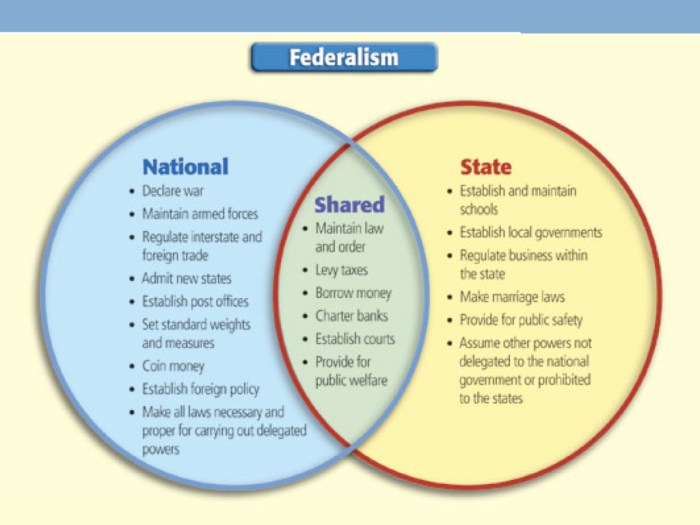
In a federal system, there are typically three levels of government: federal, state, and local. The federal government is responsible for matters of national importance, such as foreign policy, defense, and interstate commerce. State governments are responsible for matters of local concern, such as education, healthcare, and public safety.
Local governments are responsible for matters within their own jurisdictions, such as zoning, land use, and garbage collection.
The division of powers between the federal government and the state governments is typically based on the principle of enumerated powers. This means that the federal government only has the powers that are specifically granted to it by the constitution.
All other powers are reserved to the state governments.
Methods of Allocating Powers, Federalism and the division of power worksheet
There are several different methods that can be used to allocate powers in a federal system. These methods include:
- Constitutional provisions:The constitution of a federal system typically specifies the powers of the federal government and the state governments.
- Legislation:The federal government and the state governments can pass laws that allocate powers between themselves.
- Judicial interpretation:The courts can interpret the constitution and laws to determine the powers of the federal government and the state governments.
Intergovernmental Relations
The relationship between the federal government and the state governments is often complex and dynamic. There are several different types of relationships that can exist between the two levels of government, including:
- Cooperative federalism:This is a type of relationship in which the federal government and the state governments work together to achieve common goals.
- Competitive federalism:This is a type of relationship in which the federal government and the state governments compete for power and resources.
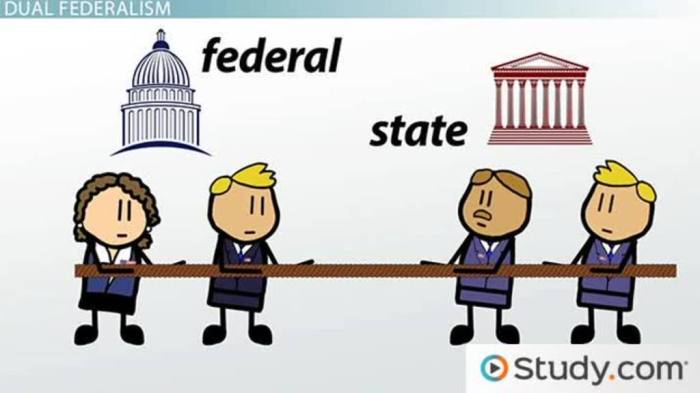
- Dual federalism:This is a type of relationship in which the federal government and the state governments have separate and distinct spheres of authority.
Case Studies of Federalism

There are many different examples of federal systems around the world. Some of the most well-known examples include:
- United States:The United States is a federal republic with a strong central government. The federal government has the power to regulate interstate commerce, declare war, and make treaties.
- Canada:Canada is a federal parliamentary democracy with a weak central government. The federal government has the power to regulate foreign policy, defense, and criminal law.
- Australia:Australia is a federal constitutional monarchy with a strong central government. The federal government has the power to regulate trade and commerce, taxation, and immigration.
Commonly Asked Questions
What is the primary purpose of a federal system?
To distribute power between a central government and multiple regional or state governments, ensuring both local autonomy and national unity.
How does the division of powers prevent tyranny?
By limiting the authority of any single entity, the division of powers ensures that no one branch of government can become overly powerful and infringe upon individual rights.
What are the key principles underlying the division of powers?
Enumerated powers, reserved powers, and the principle of subsidiarity, which allocates responsibilities to the most appropriate level of government.