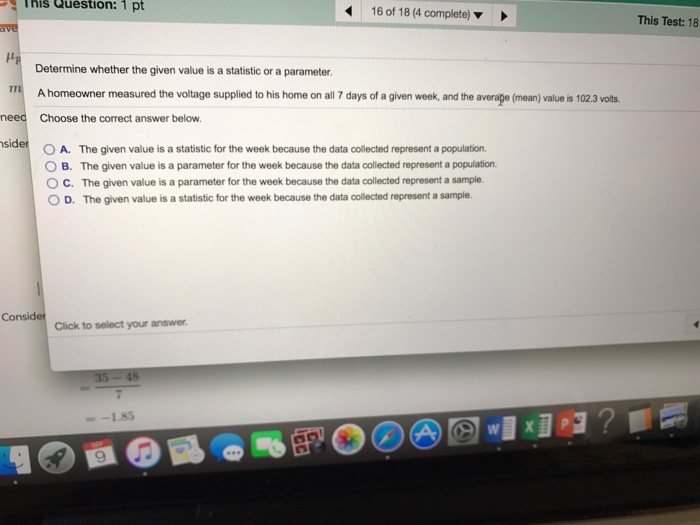
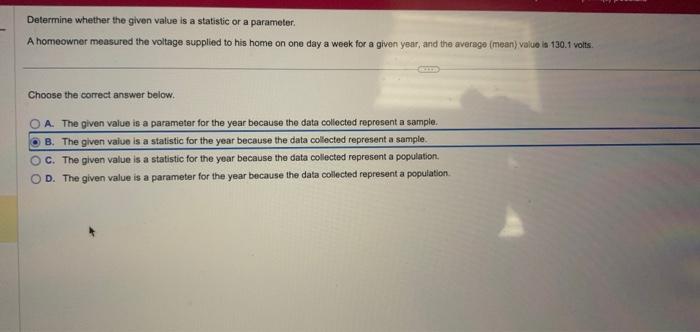
A homeowner measured the voltage supplied to their home and found it to be lower than expected. This could be a sign of a problem with the electrical system. In this article, we will discuss the different methods used to measure voltage in a home electrical system, the typical voltage levels supplied to homes in different regions, and the common voltage problems that homeowners may encounter.
We will also provide step-by-step procedures for troubleshooting voltage issues and discuss the potential causes of low or high voltage. Finally, we will provide tips and techniques for improving voltage stability and discuss the use of voltage regulators and other devices to enhance voltage quality.
Voltage Measurement Methods
Voltage measurement in a home electrical system involves determining the electrical potential difference between two points in the circuit. Various methods can be employed for this purpose:
Multimeters
Multimeters are versatile devices that measure voltage, current, and resistance. They are commonly used for electrical troubleshooting and can measure both AC and DC voltage.
Voltage Testers
Voltage testers are specialized devices designed specifically for measuring voltage. They are often used by electricians and homeowners to quickly check the presence or absence of voltage in a circuit.
Safety Precautions
When measuring voltage, it is crucial to prioritize safety. Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), such as insulated gloves and safety glasses. Ensure the circuit is de-energized before making any connections and use proper grounding techniques.
Voltage Levels and Standards
The typical voltage levels supplied to homes vary depending on the region and electrical standards. In the United States, the standard residential voltage is 120 volts (V) and 240 V for major appliances. In Europe, the standard voltage is 230 V.Voltage
levels are regulated by standards and codes to ensure safety and compatibility with electrical devices. The National Electrical Code (NEC) in the US and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) set forth guidelines for voltage levels and electrical system design.Voltage fluctuations can occur due to factors such as changes in load, power outages, or electrical faults.
These fluctuations can impact the performance and lifespan of electrical appliances. Voltage regulators can be used to mitigate voltage fluctuations and maintain a stable voltage supply.
Electrical System Components

Several components within a home electrical system influence voltage levels:
Transformers
Transformers are used to step up or step down voltage levels to match the requirements of different electrical devices. They are typically located at the entrance of the electrical service panel.
Circuit Breakers
Circuit breakers are safety devices that protect electrical circuits from overcurrent conditions. They can also interrupt the circuit if voltage levels exceed safe limits.
Fuses
Fuses are another type of safety device that protects circuits from overcurrent. They contain a thin wire that melts and breaks the circuit if the current exceeds a predetermined level.
Load
The electrical load on a circuit can affect voltage levels. When a circuit is heavily loaded, the voltage can drop due to increased resistance in the conductors.
Troubleshooting Voltage Issues
Common voltage problems in homes include:
Low Voltage
Low voltage can occur due to loose connections, overloaded circuits, or transformer issues. It can cause lights to dim, appliances to run inefficiently, and motors to overheat.
High Voltage, A homeowner measured the voltage supplied
High voltage can result from open neutrals, improper grounding, or voltage spikes. It can damage electrical devices, create electrical hazards, and increase the risk of electrical fires.
Troubleshooting Steps
To troubleshoot voltage issues:
- Check for loose connections or damaged wires.
- Verify that circuits are not overloaded.
- Inspect the transformer for any signs of damage or overheating.
- Contact a qualified electrician if the problem persists.
Voltage Optimization
Optimizing voltage levels in a home can improve electrical efficiency and extend the lifespan of appliances. Techniques for voltage optimization include:
Voltage Regulators
Voltage regulators can be installed to maintain a stable voltage supply. They can compensate for voltage fluctuations and ensure that devices receive the appropriate voltage.
Load Balancing
Balancing the electrical load across different circuits can help prevent voltage drops and improve overall system efficiency.
Energy-Efficient Appliances
Using energy-efficient appliances can reduce the electrical load and minimize voltage fluctuations.
Safety Considerations: A Homeowner Measured The Voltage Supplied

Electrical safety is paramount when dealing with voltage. Always follow these guidelines:
- Never work on live circuits without proper training and safety precautions.
- Use insulated tools and wear appropriate PPE.
- Ensure that electrical panels and outlets are properly grounded.
- Be aware of the potential hazards of electrical shocks and fires.
- If you are not comfortable working with electricity, contact a qualified electrician.
Question & Answer Hub
What is the typical voltage level supplied to homes in the United States?
The typical voltage level supplied to homes in the United States is 120 volts.
What are some of the common voltage problems that homeowners may encounter?
Some of the common voltage problems that homeowners may encounter include low voltage, high voltage, and voltage fluctuations.
What are some of the potential causes of low voltage?
Some of the potential causes of low voltage include a loose connection in the electrical system, a faulty transformer, or a problem with the power company.
What are some of the potential causes of high voltage?
Some of the potential causes of high voltage include a loose connection in the electrical system, a faulty transformer, or a problem with the power company.
What are some of the potential consequences of voltage fluctuations?
Some of the potential consequences of voltage fluctuations include damage to electrical equipment, flickering lights, and power outages.