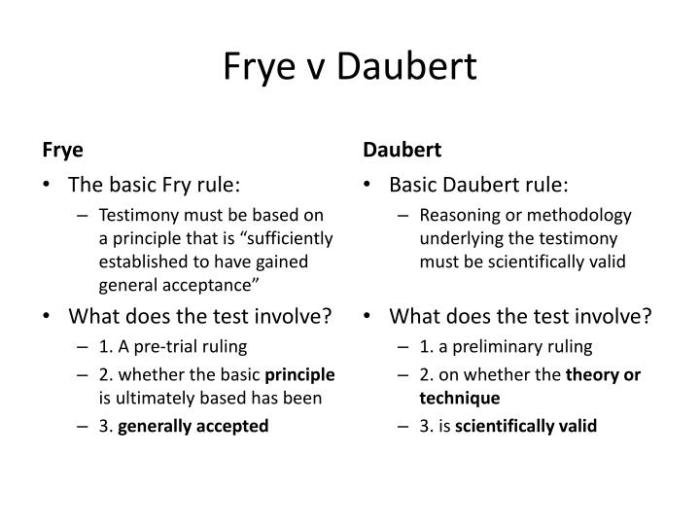
In the realm of legal evidence, the Frye vs Daubert venn diagram stands as a pivotal tool for understanding the admissibility of expert testimony. This diagram illustrates the key differences between the Frye and Daubert standards, two influential frameworks that govern the evaluation of scientific and technical evidence in court.
The Frye standard, established in 1923, focuses on the general acceptance of a scientific technique within the relevant scientific community. In contrast, the Daubert standard, adopted in 1993, emphasizes the reliability and validity of the specific methodology employed by the expert witness.
Key Differences Between Frye and Daubert Standards

The Frye standard and the Daubert standard are two different tests used to determine the admissibility of expert testimony in court. The Frye standard is based on the principle of “general acceptance” within the relevant scientific community, while the Daubert standard is based on a more flexible approach that considers the reliability and relevance of the expert’s testimony.
The Frye vs Daubert Venn diagram is a useful tool for understanding the differences between the two approaches to expert testimony. If you’re looking for more information on this topic, I recommend checking out the nr 360 quiz 1 chamberlain . This resource provides a comprehensive overview of the Frye vs Daubert debate, and it can help you better understand the nuances of each approach.
Returning to the Frye vs Daubert Venn diagram, it’s important to note that…
One of the key differences between the Frye and Daubert standards is the way in which they define “general acceptance.” Under the Frye standard, general acceptance means that the expert’s testimony is based on a technique or methodology that has been widely accepted by the relevant scientific community.
Under the Daubert standard, general acceptance is not a requirement, and the court may consider other factors, such as the reliability and relevance of the expert’s testimony, in determining its admissibility.
Examples of Frye and Daubert Applications
The Frye standard is still used in some jurisdictions, such as California and New York. In People v. Kelly, the California Supreme Court held that expert testimony on the reliability of eyewitness identification was admissible under the Frye standard because it was based on a technique that had been widely accepted by the scientific community.
The Daubert standard is used in the majority of federal courts and in most state courts. In Daubert v. Merrell Dow Pharmaceuticals, Inc., the U.S. Supreme Court held that expert testimony on the link between Bendectin and birth defects was inadmissible because it was not based on reliable scientific evidence.
Admissibility of Expert Testimony
Expert testimony plays a crucial role in both Frye and Daubert cases. However, the two standards differ in their approach to determining the admissibility of such testimony.
Under the Frye standard, expert testimony is admissible if it is based on “scientific knowledge” that is “generally accepted” within the relevant scientific community. This test focuses on the consensus within the field rather than the reliability of the specific expert’s methodology.
Examples of Admissibility under Frye
- In Frye v. United States(1923), the court excluded expert testimony on the systolic blood pressure deception test because it was not generally accepted within the scientific community at the time.
- In Daubert v. Merrell Dow Pharmaceuticals(1993), the court admitted expert testimony on the link between Bendectin and birth defects, even though there was no consensus within the scientific community, because the expert’s methodology was sound and reliable.
Frye and Daubert in Practice: Frye Vs Daubert Venn Diagram
The Frye and Daubert standards are two distinct approaches to assessing the admissibility of expert testimony in court. In practice, these standards are applied in different ways, leading to both challenges and controversies.
Challenges and Controversies, Frye vs daubert venn diagram
- Frye Standard:The Frye standard is often criticized for being too rigid and exclusionary, as it requires a new scientific technique to be “generally accepted” within the relevant scientific community before it can be admitted as evidence.
- Daubert Standard:The Daubert standard is more flexible and allows judges to consider a wider range of factors when assessing the admissibility of expert testimony, but it has also been criticized for being too subjective and unpredictable.
Case Studies
- Frye Standard:In Frye v. United States(1923), the Frye standard was used to exclude expert testimony about the results of a lie detector test because the test was not “generally accepted” within the scientific community.
- Daubert Standard:In Daubert v. Merrell Dow Pharmaceuticals, Inc.(1993), the Daubert standard was used to admit expert testimony about the link between a drug and birth defects, even though the testimony was not based on a single, generally accepted scientific method.
Comparison of Frye and Daubert
The Frye and Daubert standards are two different tests used to determine the admissibility of expert testimony in court. Both standards require the judge to make a preliminary assessment of whether the expert testimony is reliable and relevant, but they differ in their specific requirements.
The following table compares the key features of the Frye and Daubert standards:
| Feature | Frye Standard | Daubert Standard |
|---|---|---|
| Admissibility criteria | General acceptance in the relevant scientific community | Reliability and relevance |
| Burden of proof | Proponent of the evidence (party offering the expert testimony) | Proponent of the evidence (party offering the expert testimony) |
| Role of the judge | Gatekeeper: Decides whether the expert testimony is admissible | Gatekeeper: Decides whether the expert testimony is admissible |
| Role of the jury | Weighs the expert testimony along with other evidence | Weighs the expert testimony along with other evidence |
The Frye standard is a more lenient standard than the Daubert standard. Under the Frye standard, expert testimony is admissible if it is generally accepted in the relevant scientific community. This means that the expert testimony must be based on a well-established body of scientific knowledge.
The Daubert standard, on the other hand, is a more rigorous standard. Under the Daubert standard, expert testimony is admissible if it is reliable and relevant. This means that the expert testimony must be based on sound scientific principles and methods, and it must be relevant to the issues in the case.
Future of Frye and Daubert
The future of the Frye and Daubert standards remains uncertain, as they are constantly being challenged and refined by courts. However, there are several potential developments that could impact the standards in the coming years.
Emerging Trends and Issues
One emerging trend is the increasing use of expert testimony in a wide variety of cases. This is due in part to the growing complexity of the issues being litigated, as well as the increasing availability of experts in various fields.
As a result, courts are being forced to grapple with the challenges of determining the admissibility of expert testimony.Another emerging trend is the use of new technologies to analyze data and generate expert opinions. This is raising new questions about the reliability and validity of expert testimony, as well as the role of judges in evaluating such testimony.
Potential Impact of Legal Developments
Several recent legal developments could also impact the Frye and Daubert standards. For example, the Supreme Court’s decision in Daubert v. Merrell Dow Pharmaceuticals, Inc.has been interpreted by some courts as limiting the admissibility of expert testimony. However, other courts have continued to apply the Frye standard, or have adopted a more flexible approach to the admissibility of expert testimony.The
future of the Frye and Daubert standards is likely to be shaped by the interplay of these emerging trends and legal developments. It is possible that the standards will continue to evolve, as courts seek to balance the need for reliable expert testimony with the need to protect against the admission of junk science.
FAQ Section
What is the key difference between the Frye and Daubert standards?
The Frye standard focuses on the general acceptance of a scientific technique within the relevant scientific community, while the Daubert standard emphasizes the reliability and validity of the specific methodology employed by the expert witness.
Which standard is more widely accepted today?
The Daubert standard has gained wider acceptance due to its more rigorous approach to ensuring the reliability of expert evidence.
How does the Frye vs Daubert venn diagram help in understanding expert testimony?
The diagram illustrates the key differences between the Frye and Daubert standards, making it easier to compare and contrast their approaches to the admissibility of expert testimony.